You’ve probably come across jojoba oil on the ingredient labels of one or more of your skincare products. This multitasking natural extract can be used as a moisturizer, makeup remover, lip balm, sunburn treatment, face wash, and much more. It’s a useful all-around skin saver that comes in many forms.
The molecular configuration of jojoba oil is quite different from other oils. It is biocompatible, meaning it can easily penetrate and absorb into the skin. Many people use jojoba oil as part of their daily skincare routine.
|
The Basics Jojoba oil is a fast-absorbing, non-greasy plant extract that can rapidly moisturize, cleanse, and exfoliate the skin. It is widely used in skincare products, with wide-ranging benefits including:
|
What Is Jojoba Oil?

Jojoba oil is obtained from the seeds of the jojoba plant (also known as goat nut or wild hazel), a shrub native to the Southwestern United States and Baja California. The oil has a thick, waxy consistency. In fact, jojoba oil is actually wax at the molecular level.
Known for its long shelf life and strong resistance to high temperatures, jojoba oil is a very common ingredient in beauty products such as moisturizers, body lotions, body washes, shampoos, and conditioners.
The product can directly be applied to your skin directly. It is easily absorbed through the superficial layers of the skin, making it an easy and effective skincare ingredient.
Can I Use Jojoba Oil As a Moisturizer?
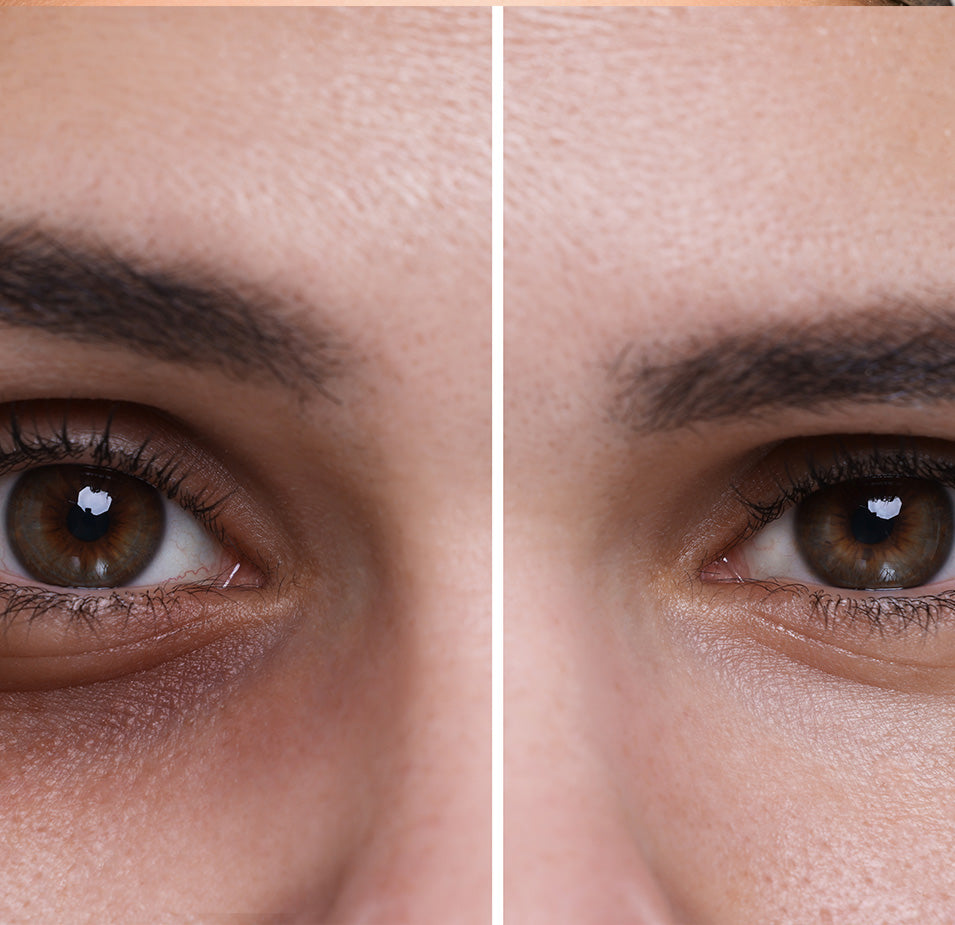
Jojoba oil is an excellent natural moisturizer both on its own and as an ingredient in skincare formulations. It’s an especially useful remedy for fighting skin changes that occur as a result of harsh, dry winter weather.
There are multiple benefits of using jojoba oil as a facial moisturizer. Jojoba oil contains iodine, which protects your delicate skin against bacteria and harmful microorganisms. It is also rich in vitamin E and B-complex vitamins, which enhance and improve the skin's immune resistance while facilitating the rapid healing of wounds and lesions. If you suffer from dry skin, jojoba oil can help prevent cracks and rashes.
In addition to essential vitamins and minerals, jojoba oil along with various other nutritious antioxidants that function as humectants. Humectants are water loving-ingredients known for their moisture-retaining capacity. Jojoba oil draws water particles to your skin and seals the moisture in, giving the skin a dewy glow.
Jojoba oil also helps control excessive oil secretion from the skin glands. Because jojoba oil is so good at keeping the skin well-hydrated, the body scales back its natural process of sebum production when the ingredient is applied. Thus, jojoba oil deeply moisturizes your skin and leaves behind a soothing, protective layer without looking or feeling greasy.
Does Jojoba Oil Help Acne?
Unlike other herbal and natural oils, jojoba oil has the additional benefit of treating acne and other skin conditions.
Jojoba oil is classified as a gentle exfoliating agent, which acts as a deep skin cleanser to reduce acne as well as acne-related hyperpigmentation and scarring. Acne treatment formulations usually contain ingredients like azelaic acid, kojic acid, and alpha-hydroxy acids along with a mild exfoliant like jojoba oil to battle acne without further damaging the skin.
Gentle exfoliation with jojoba oil helps remove cellular debris to prevent the build-up of dead skin cells. Because the ingredient is so mild, side effects like skin irritation or over-exfoliation are rare. This makes it a safe product for those with acne-prone or sensitive skin.
Most oils are greasy and can have a tendency to clog skin pores, resulting in breakouts and acne. In contrast, jojoba oil is a non-greasy, fast-absorbing product that does not clog pores. Some jojoba oil formulations are not actually oils at all. An organic compound called an ester can be created by combining a fatty acid (jojoba oil) with fatty alcohol (hydrogenated jojoba oil). These two particles restructure themselves through a process known as interesterification, producing a new compound that is oil-free but delivers the same moisturizing benefits as oil.
If your skin tends to be oily or you suffer from acne, jojoba oil, especially the processed, oil-free version, can be an excellent way to softly cleanse and moisturize your skin.
Fighting Damage From Sun Exposure
If you’re soaking up a lot of sun rays, jojoba oil could be a highly beneficial addition to your skincare routine before and after spending time outdoors. Applied before sun exposure, jojoba oil protects can protect your skin from damaging UV rays; applied after, it soothes and replenishes dry, inflamed skin while preventing the development of pigmentation.
Jojoba oil has a modest sun protection factor (SPF) of 4 and is often used in sunscreen products. Combined with higher SPF ingredients, it can help provide a strong barrier against sunburn and associated damage. It also serves to minimize the impact of UV exposure on collagen degradation, thereby delaying the onset of wrinkles and other signs of photoaging.
Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Benefits
Jojoba oil is rich in highly nutritious vitamins, along with antioxidants and minerals such as chromium, copper, and zinc. All of these components are superstar ingredients for nourishing and protecting your skin.
Because of its impressive nutrient profile, jojoba oil can treat aid in the treatment of a variety of ailments associated with hungry or damaged skin. The antioxidant properties found in jojoba oil can contribute to healing eczema, psoriasis, and other skin conditions while soothing dryness, itching, scaling, and oozing. In addition, the powerful antioxidant vitamin E fights cell damage caused by exposure to environmental stressors like toxins, pollutants, and dust, preventing the onset of premature aging.
FAQs
Is jojoba oil safe?
Jojoba oil is safe to use, and allergic reactions are very rare as compared to other botanical essential oils. However, for those with sensitive skin, almost anything can cause an allergic reaction—including environmental factors like water and sunshine. Diet can also affect the intensity of allergic reactions. When allergic reactions occur, symptoms may include redness, hives, and itching. To avoid unexpected adverse reactions, it’s a good idea to try introducing new skincare products gradually with a patch test before incorporating it into your skincare routine.
What’s the best way to use jojoba oil for skin?
Unlike other essential oils, jojoba oil can be directly applied to the skin without any dilution. The nature and method of application depend on your intended result. For example, it can be massaged all over the face before bedtime as an anti-aging serum and moisturizer, applied to the lips as a lip balm, used as a cleansing rinse in the morning followed by water, or combined with other ingredients in any number of sun protection products.
References
- Sandha, G. K., & Swami, V. K. (2009). Jojoba oil as an organic, shelf stable standard oil-phase base for cosmetic industry. Rasayan J Chem, 2(2), 300-306.
- Pazyar, N., Yaghoobi, R., Ghassemi, M. R., Kazerouni, A., Rafeie, E., & Jamshydian, N. (2013). Jojoba in dermatology: a succinct review. Giornale italiano di dermatologia e venereologia: organo ufficiale, Societa italiana di dermatologia e sifilografia, 148(6), 687-691.
- Matsumoto, Y., Ma, S., Tominaga, T., Yokoyama, K., Kitatani, K., Horikawa, K., & Suzuki, K. (2019). Acute effects of transdermal administration of jojoba oil on lipid metabolism in mice. Journal Medicina, 55(9), 594.
- Hahn, H. J., Jung, H. J., Schrammek Drusios, M. C., Lee, S. N., Kim, J. H., Kwon, S. B., & Ahn, K. J. (2016). Instrumental evaluation of anti-aging effects of cosmetic formulations containing palmitoyl peptides, Silybum marianum seed oil, vitamin E and other functional ingredients on aged human skin. Experimental and therapeutic medicine, 12(2), 1171-1176.
- Linder, J. (2013). Daily Care for Acne, Hyperpigmentation, Aging, and Sensitive Skin. Plastic Surgical Nursing, 33(4), 172-176.
- Sawant, O., & Khan, T. (2020). Management of periorbital hyperpigmentation: An overview of nature-based agents and alternative approaches. Dermatologic Therapy, 33(4), e13717.