As complicated as it may sound, niacinamide is actually just a form of vitamin B3, an important nutrient found in everyday foods like meat, dairy, and green veggies. Applied as skincare, niacinamide is one mighty vitamin with powerful anti-inflammatory properties that protect skin and help reverse the effects of aging.
|
The Basics Niacinamide, the superpower B3 derivative, helps protect your skin’s appearance, texture, and tone. Its host of benefits include:
|
What Is Niacinamide?
Niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide, is a water-soluble vitamin that dissolves easily within the tissues of the body. This quick and easy absorption process makes it a great oral supplement, and potent addition to any topical skincare routine.
Pop it as a vitamin, and you’ll see benefits like healthier skin, nails, and hair. Applied directly to your skin, niacinamide packs a powerful anti-inflammatory punch to zap skin discoloration and pigmentation, and improve the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
You can find niacinamide in many skincare products such as cleansers, toners, exfoliators, serums, moisturizers, and even sunscreen.
The Science Behind Niacinamide Skincare Benefits
Protection Against Dry Skin
Niacinamide strengthens the skin barrier and protects it against harsh climates that can sap moisture. The science behind this involves trans-epidermal water loss, the amount of water that evaporates off the skin’s surface. Niacinamide reduces this water loss, which defends against skin dehydration and dryness. It also helps keep the skin’s natural sheen by regulating the oil production from sebaceous glands.
This versatile vitamin is a must-have for those living in harsh winter climates, and anyone battling dry skin. Other ingredients that can complement and enhance its moisturizing effect include glycerin, sodium PCA, and sodium hyaluronate. For those seeking the hydrating benefits of niacinamide, consider looking for it in a moisturizer.
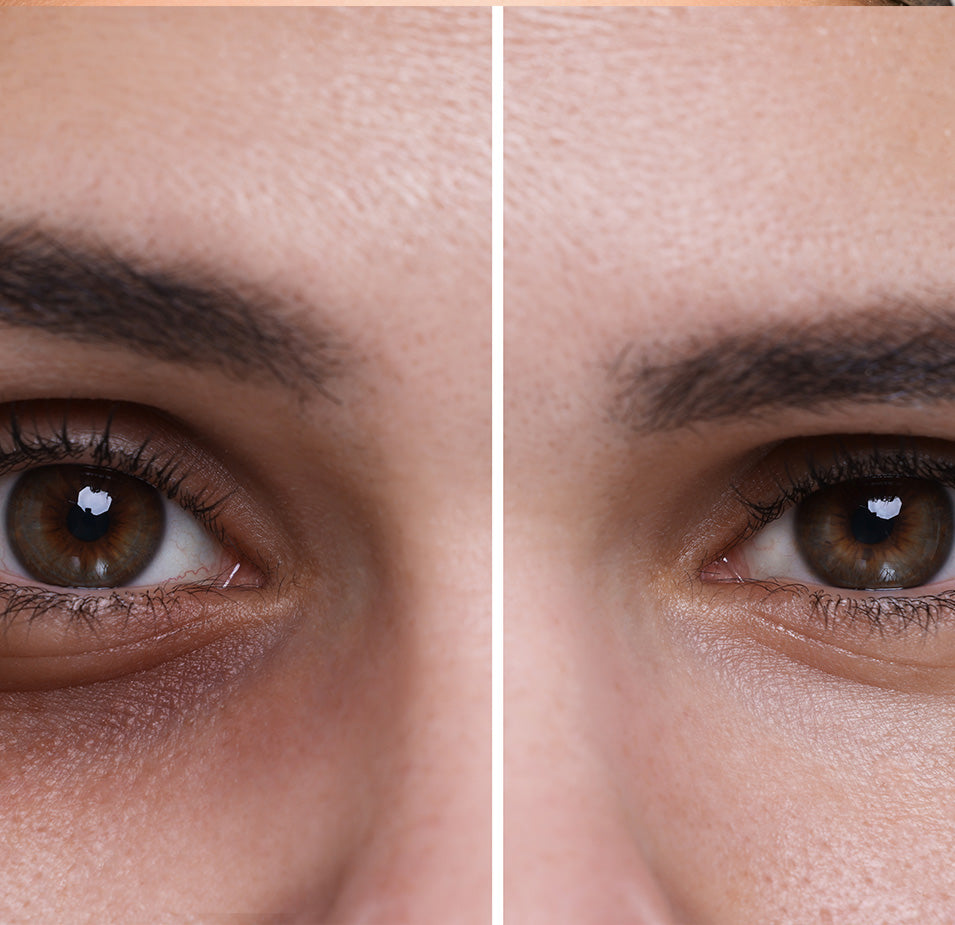
Anti-Aging Benefits
Niacinamide is a potent anti-aging ingredient that helps reduce fine lines and wrinkles while improving skin elasticity. To measure niacinamide’s impact, researchers look at photoaging, a measure of skin’s appearance based on sun exposure. Studies of niacinamide show it can reduce and improve 5 features of photoaging:
- Wrinkles
- Yellowing skin tone
- Blotchiness
- Poor texture
- Fine Lines
How does niacinimide enact its age-reversing powers? Studies show that Niacinamide fights signs of aging on multiple fronts:
- It increases the creation and differentiation of skin proteins like keratin, which stabilize skin and keep it looking youthful.
- It also amps up production of essential skin lipids called ceramides, which help to plump and firm skin.
- Its antioxidant properties fend off free radicals: unstable atoms which, left to their own devices, can damage cells and accelerate aging.
Improving Skin Appearance
Besides its extensive anti-aging benefits, Niacinamide also helps improve overall skin appearance by:
- Shrinking enlarged pores
- Lessening hyperpigmentation
- Reducing inflammation and redness
While niacinamide improves your skin’s texture by plumping and firming skin, it also helps by treating enlarged, open pores. When oil and dirt get trapped in the skin, the superficial layers of skin appear rough and bumpy, known informally as “orange peel skin.”

This increases the risk of breakouts and acne, and can lead to hyperpigmentation, inflammation, and more clogged pores. Niacinamide stops this cycle in its tracks by tightening and shrinking pores.
Niacinamide is a powerful skin lightening agent that does wonders in acne-prone, sun-damaged, hyperpigmented and sun-tanned skin. Niacinamide and vitamin C can be paired, along with retinol and tranexamic acid, to increase lightening benefits.
Last but not least, Niacinamide’s powerful anti-inflammatory properties help manage redness and flares associated with eczema, rosacea, and acne.
FAQs
Is Niacinamide safe?
Niacinamide is a very safe, water-soluble vitamin that can be consumed with no serious risk of side effects.
How long does it take to see results?
Usually, it takes 3- 5 days of regular use before you can notice any improvement in your skin with Niacinamide use; however, it also depends on the severity of cosmetic issues and the concentration you use. Even if it takes a bit longer, regular Niacinamide use is associated with promising results for all skin types.
If we can take Niacinamide orally, why should we use it in skin products?
We can get Niacinamide through our diet, but topical application is associated with a variety of anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and skin brightening benefits. Niacinamide’s water solubility makes it ideal for incorporating into topical and anti-aging products and is a common ingredient in skin care products and cosmetics.
How and when should Niacinamide be applied?
It works great with other powerful ingredients like the hydrating hyaluronic acid, and skin exfoliants like AHAs (alpha-hydroxy acids) and BHAs (beta hydroxy acid).
To achieve maximum benefits, niacinamide should be incorporated in the daily skin care routine. It can be helpful to adopt a multi-ingredient approach for your skin, as single ingredients may not provide all the cosmetic benefits your skin needs. You can find Niacinamide in:
- Cleansers
- Toners
- Exfoliators
- Skin care serums and moisturizers
- Sunscreen SPF 30 or more
Conclusion
This versatile vitamin is great for treating issues of tone, texture, and overall appearance. It works like a shield to protect your skin against harsh environmental factors, from cold, dry air to bright, sunny skies. It helps keep pores small to fight dirt and grime, and its antioxidant properties keep inflammation at bay. Niacinamide is a safe and potent addition to your daily skincare routine.
References
- Gehring, W. (2004). Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. Journal of cosmetic dermatology, 3(2), 88-93.
- Draelos, Z. D., Matsubara, A., & Smiles, K. (2006). The effect of 2% niacinamide on facial sebum production. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy, 8(2), 96-101.
- Bissett, D. L., Oblong, J. E., & Berge, C. A. (2005). Niacinamide: AB vitamin that improves aging facial skin appearance. Dermatologic surgery, 31, 860-866.
- Hakozaki, T., Minwalla, L., Zhuang, J., Chhoa, M., Matsubara, A., Miyamoto, K., ... & Boissy, R. E. (2002). The effect of niacinamide on reducing cutaneous pigmentation and suppression of melanosome transfer. British Journal of Dermatology, 147(1), 20-31.
- Bissett, D. L., Miyamoto, K., Sun, P., Li, J., & Berge, C. A. (2004). Topical niacinamide reduces yellowing, wrinkling, red blotchiness, and hyperpigmented spots in aging facial skin. International journal of cosmetic science, 26(5), 231-238.
- Wohlrab, J., & Kreft, D. (2014). Niacinamide-mechanisms of action and its topical use in dermatology. Skin pharmacology and physiology, 27(6), 311-315.